Lung Cancer
🫁 What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a disease that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air passes through the nose, down the windpipe (trachea), and into the lungs, where it travels through tubes called bronchi. Most lung cancers begin in the cells that line these tubes.
Types of Lung Cancer:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Most common type.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Accounts for about 20% of all lung cancer cases.
Mixed Small Cell/Large Cell Cancer: Contains both types.
Metastatic Cancer to the Lung: Starts in another part of the body and spreads to the lungs.
🚬 Causes of Lung Cancer
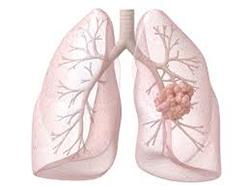
Lung cancer is the deadliest form of cancer for both men and women. More people die from lung cancer each year than from breast, colon, and prostate cancers combined.
It is more common in older adults and rare in individuals under 45 years old.
Major Risk Factors Include:
Cigarette smoking: Leading cause of lung cancer. Risk increases with quantity and duration of smoking.
Second-hand smoke: Inhaling smoke from others.
Exposure to carcinogens: Such as asbestos, uranium, diesel exhaust, and more.
Family history of lung cancer
Radiation therapy to the chest
Air pollution and arsenic in water
Radon gas exposure
⚠️ Symptoms of Lung Cancer
In its early stages, lung cancer may not cause any symptoms. As it progresses, symptoms vary based on the type and spread of cancer.
Common Symptoms Include:
Persistent chest pain
Chronic cough
Coughing up blood
Shortness of breath
Wheezing
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and loss of appetite
Late-Stage Symptoms:
Bone pain or tenderness
Facial paralysis or swelling
Hoarseness or voice changes
Joint pain
Nail changes
Difficulty swallowing
Shoulder pain
Weakness
Note: These symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis.
🧪 Exams and Tests for Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is often detected through a chest X-ray or CT scan performed for unrelated reasons.
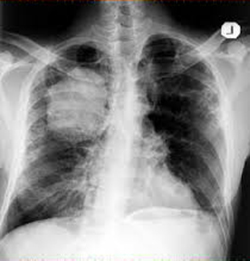
Your doctor will perform a physical examination and gather a detailed medical history, including:
Smoking history
Exposure to harmful substances
Family history
During the exam, your doctor may listen for fluid around the lungs, which can suggest cancer.
Diagnostic Tests:
Chest X-ray and CT scan
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
MRI or PET scan
Sputum cytology
Bone scan
Thoracentesis (fluid sample)
Biopsy (tissue sampling)
Biopsy Methods:
Bronchoscopy with biopsy
CT-guided needle biopsy
Endoscopic oesophageal ultrasound (EUS)
Mediastinoscopy
Open lung biopsy
Pleural biopsy
After diagnosis, further imaging tests determine the stage of cancer — indicating tumour size and how far it has spread. Staging helps guide treatment.
🩺 Lung Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment depends on:
The type of lung cancer
The stage of cancer
Your overall health
Available Treatments:
Surgery: Removal of tumour if cancer hasn’t spread.
Chemotherapy: Drugs to kill cancer cells and prevent their growth.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
These treatments may be used alone or in combination. Your doctor will customize your treatment plan and explain the approach suited to your diagnosis.
Ready to get our medical care? We’re always wait for serve you, Make an Appointment.
Appointment
Our Pricing Packages
- Neurology Care
- Medical Care
- Child & Old Care
- Dental Care
- On-Time Delivery
- Neurology Care
- Medical Care
- Child & Old Care
- Dental Care
- On-Time Delivery
- Neurology Care
- Medical Care
- Child & Old Care
- Dental Care
- On-Time Delivery
